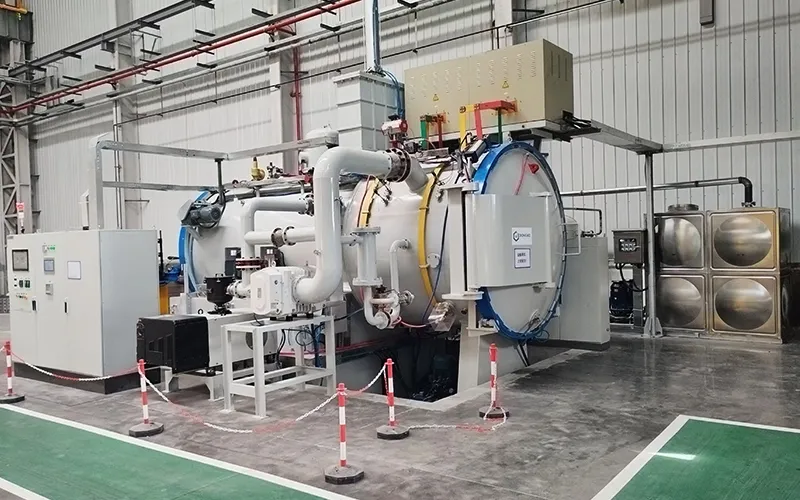
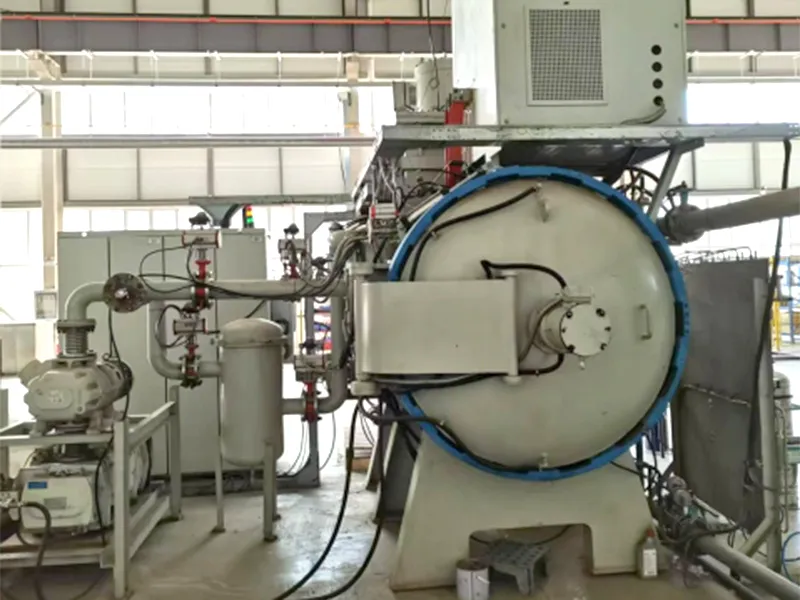
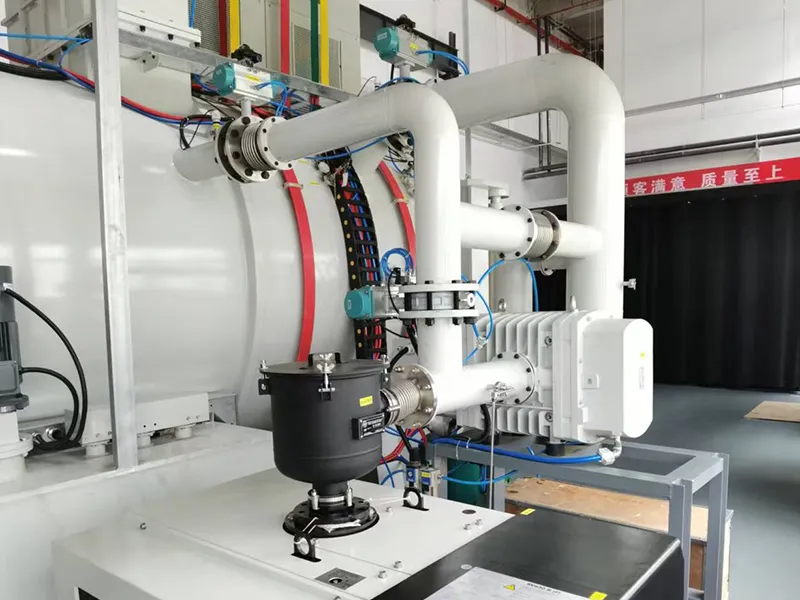
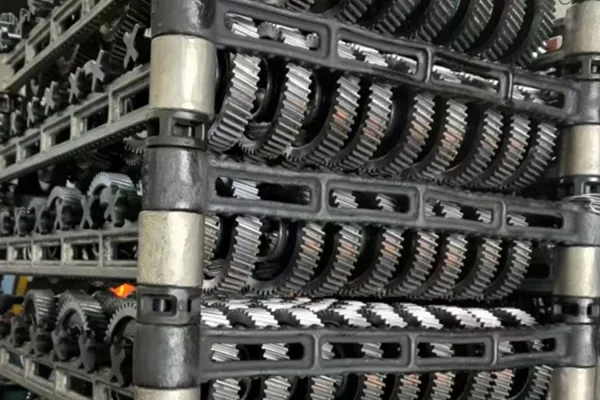
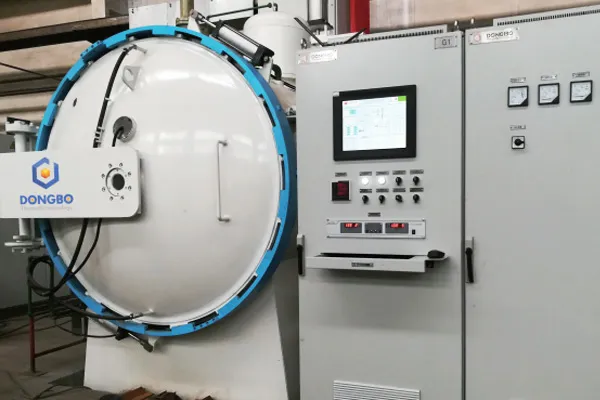
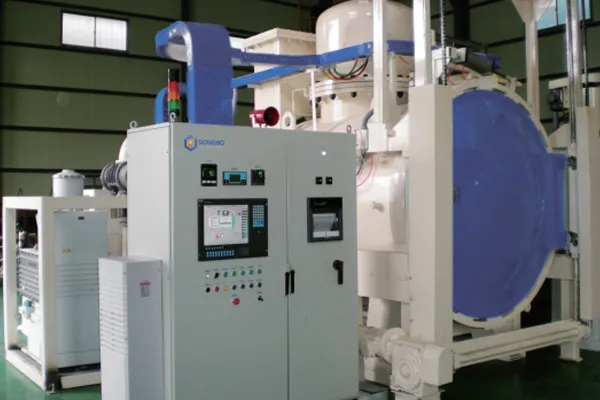
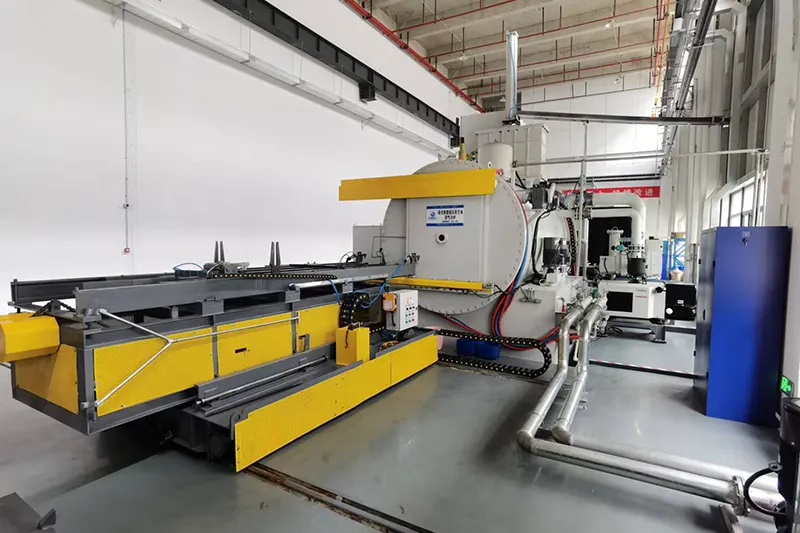
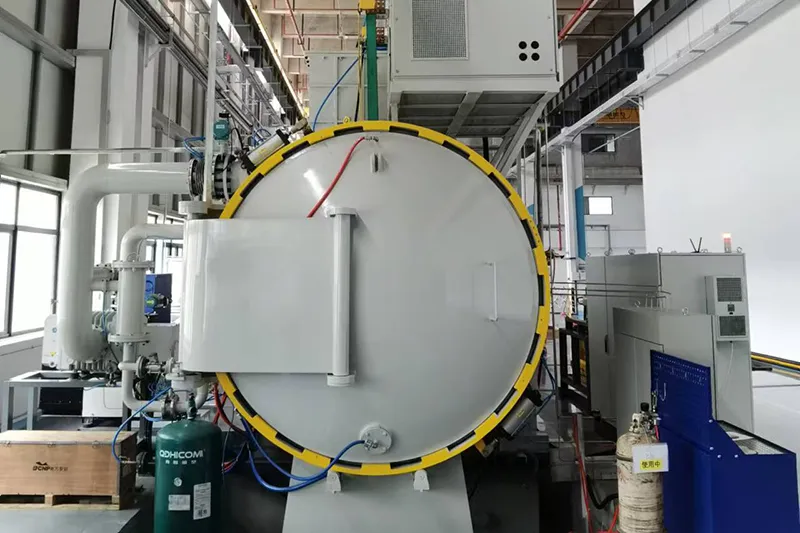
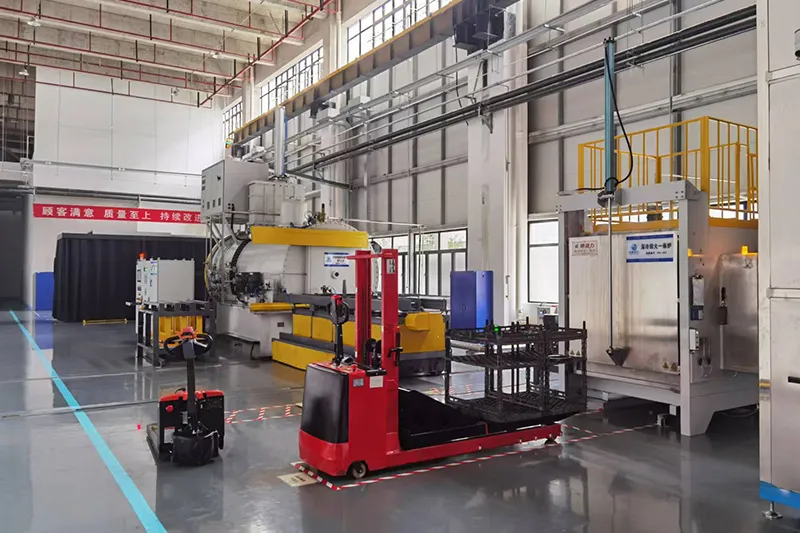
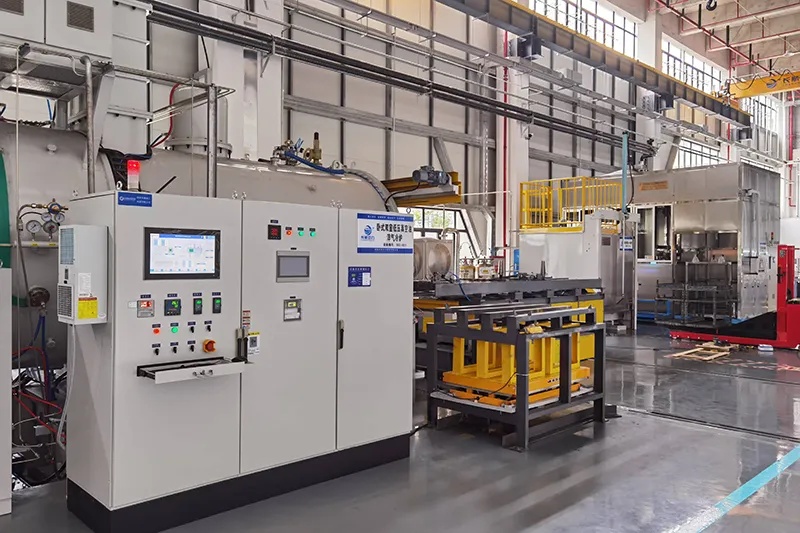
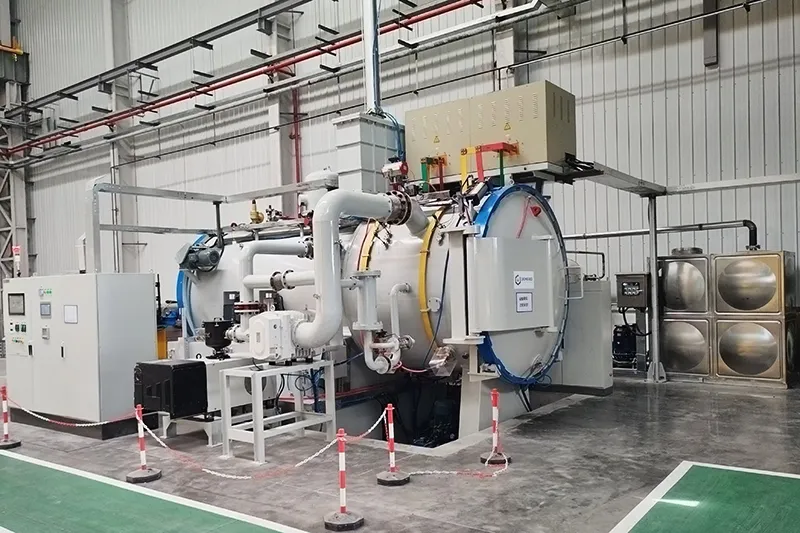
- Applications
- Specifications
- Advantages
- Process
- Features
- Examples
- Commitments
Applications
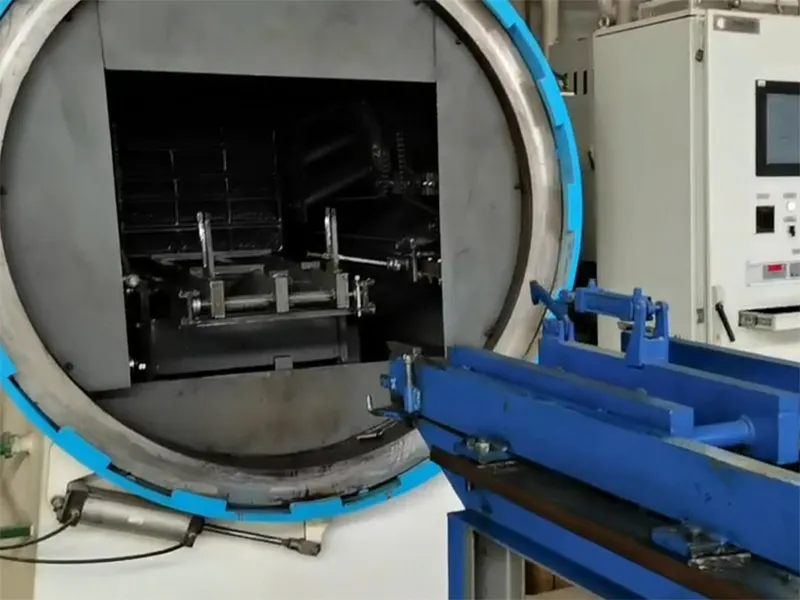
Low pressure vacuum carburizing (LPC) is a case hardening process performed in a vacuum furnace using hydrocarbon gases at low pressure and elevated temperatures. It is designed to form a hardened surface layer while maintaining a tough core, enhancing fatigue life and improving the wear resistance of high-value components that require precise carburizing or carbonitriding, such as gears and shafts. Additionally, it is suitable for vacuum quenching and annealing of materials like high-speed steel, tool steels, and alloy structural steels.
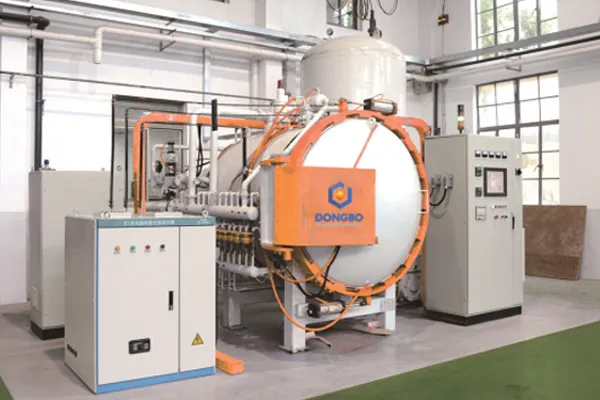
Specifications
| Model | DB-DCO644H | DB-DCO755H | DB-DCO966H | DB-DCO1266H | DB-DCO1299H |
| Effective internal dimensions (mm) | 600×400×400 | 700×500×500 | 900×600×600 | 1200×600×600 | 1200x900x900 |
| Max. load capacity (kg) | 200 | 300 | 500 | 800 | 1500 |
| Heating power (kW) | 60/65 | 75/85 | 105/120 | 140/160 | 250/270 |
| Max. temperature (℃) | 1200/1320 | 1200/1320 | 1200/1320 | 1200/1320 | 1200/1320 |
| Ultimate vacuum level (Pa) | 4×10⁻¹/4×10⁻³ | 4×10⁻¹/4×10⁻³ | 4×10⁻¹/4×10⁻³ | 4×10⁻¹/4×10⁻³ | 4×10⁻¹/4×10⁻³ |
| Temperature uniformity (℃) | ±5 | ±5 | ±5 | ±5 | ±5 |
| Max. cooling gas pressure (bar) | 1.99 | 1.99 | 1.99 | 1.99 | 1.99 |
| Surface carbon concentration (%) | ±0.05 | ±0.05 | ±0.05 | ±0.05 | ±0.05 |
| Hardness tolerance (HRC) | ±1.5 | ±1.5 | ±1.5 | ±1.5 | ±1.5 |
| Pressure rise rate (Pa/h) | 0.5/0.27 | 0.5/0.27 | 0.5/0.27 | 0.5/0.27 | 0.5/0.27 |
| Transfer time (S) | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 39 |
Note: The above parameters are for the standard horizontal double-chamber oil quenching low-pressure vacuum carburizing furnace. We can provide customized, non-standard designs and manufacturing to meet specific customer requirements, such as achieving an ultimate vacuum level of 10⁻⁴ Pa or higher and a pressure rise rate better than 0.1 Pa/h.
Advantages
Key Advantages
- Safe and eco-friendly with constrained open flames or explosion risks.
- The furnace can be started and stopped at any time.
- High-quality carburized layer with minimal internal oxidation and superior layer performance.
- Optimized for blind hole carburizing, it is suitable for components like fuel injector parts, ensuring uniform layer distribution.
- Carburizing temperatures reach up to 1050°C, making it ideal for stainless steel and deep-layer carburizing.
- Superior surface quality & low distortion to ensure minimal quenching deformation and high-quality surface finish.
- Reduced gas consumption, shorter carburizing cycles, and lower operational costs.
Technical Advantages
- Dynamic carbon flux adjustment
We have developed a dynamic optimization method for carbon flux, ensuring precise control for materials with complex alloy compositions. It reduces carbon black formation, minimizing maintenance time and enhancing process efficiency.
- Proprietary alloy mathematical model
By analyzing thermodynamic and kinetic principles, we have analyzed and optimized the diffusion coefficient model, reducing the carburizing prediction error from the national standard of 20% to just 5%.
- Hardness gradient flexible control technology
This technology enables adjustable hardness gradients in the high-hardness zone (HV≥680) within a 30%-80% range, catering to customization for specific service environments. Especially for precision reduction geas, it maintains high hardness even after wear, significantly extending service life.
- Supplementary carburizing technology
In cases of unexpected issues like power outages or gas interruptions, the system can perform supplementary carburizing to ensure process consistency.
- Precise carburizing time control
Utilizing a forced gas washing process and an optimized vacuum system with short extraction pipelines, the furnace minimizes the impact of residual acetylene during pulse intervals, significantly reducing the transition time from carburizing to diffusion. This allows for precise control of carburizing time (as fine as 5 seconds), achieving a prediction accuracy of over 95%. The carburized layer structure is controlled to achieve levels below grade 2, minimizing residual carbide and retained austenite for optimal results.
- Optimized simulation model design
We have introduced a supersonic high-temperature jet flow control method, optimizing the heating and gas inflation/deflation systems. The newly developed 1299 vacuum low-pressure carburizing system (1200×900×900 mm) ensures uniform treatment for large workpieces, promoting efficient and resource-saving production.
- China’s first proprietary intelligent process expert system
This system enables intelligent process generation and management, significantly reducing reliance on operator expertise. The carburizing case depth prediction error is controlled within 5%, achieving superior outcomes for carbide and retained austenite levels.
- Dense loading technology
Through process flow and temperature field simulations, we have developed personalized carburizing system designs, ensuring uniform carburizing even under dense loading conditions.
- Unattended intelligent operation
The system can be configured with multiple automatic material handling vehicles, enabling unattended, fully automated operation with seamless coordination across multiple devices.
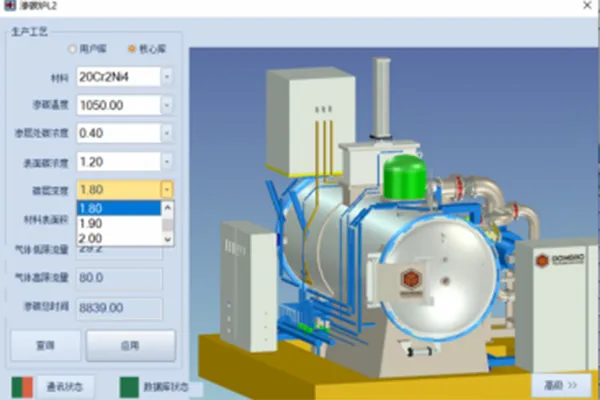
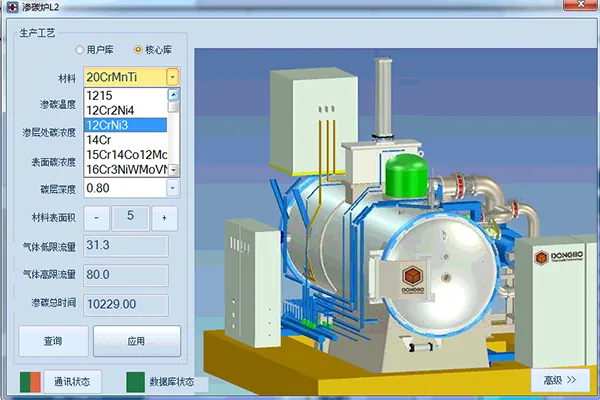
Process selection examples from the intelligent process expert system
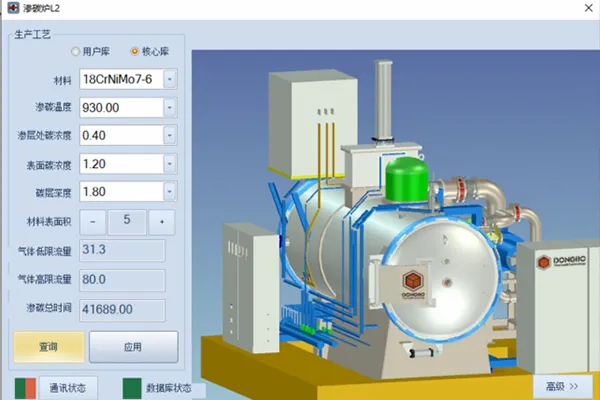 18CrNiMo7-6 1.8mm carburizing process
18CrNiMo7-6 1.8mm carburizing process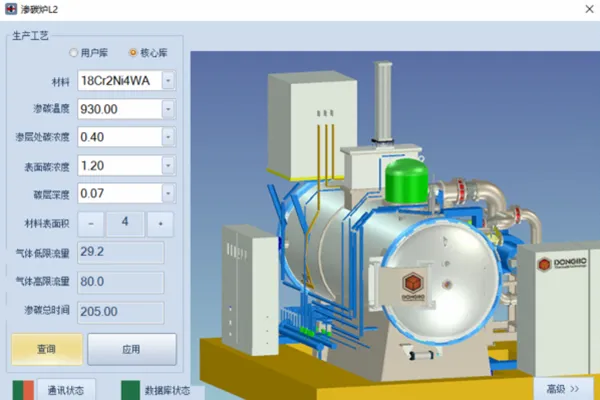 18Cr2Ni4W 0.07mm carburizing process
18Cr2Ni4W 0.07mm carburizing process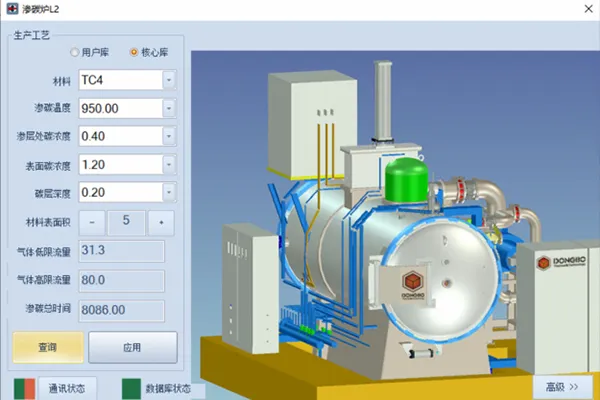 TC4 0.2mm carburizing process
TC4 0.2mm carburizing process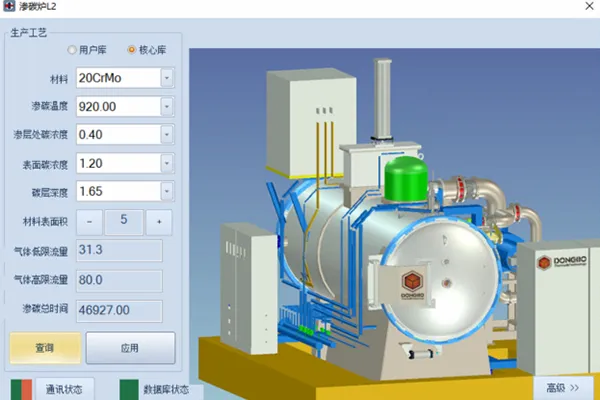 20CrMoH 1.65mm carburizing process
20CrMoH 1.65mm carburizing process
Features
The database allows selection of different case depths from 0.01mm to 8mm, meeting diverse material processing requirements.
The intelligent process Expert System includes a comprehensive database of carburizing processes for various materials. If a material is not indexed, the system automatically adapts based on material composition, allowing seamless integration.
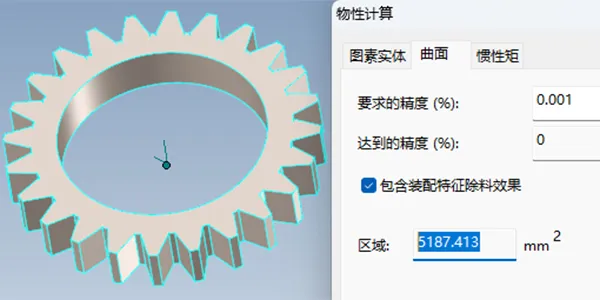
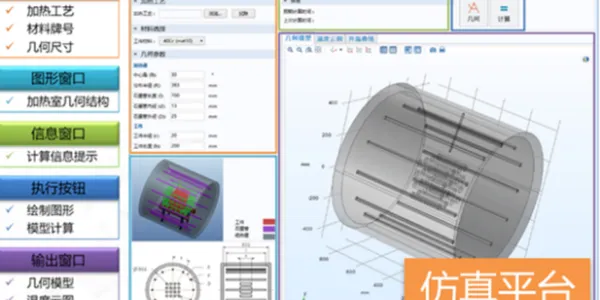
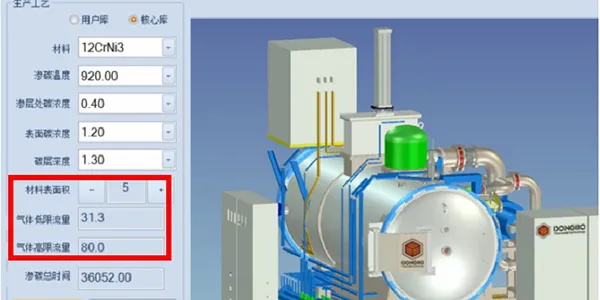
The carburizing process expert system features a dedicated surface area calculation method and software. It uses finite element modeling (FEM) or commercial design software to determine part surface area, enabling precise adjustment of gas flow rate for optimized carburizing. A surface area database is built for users to efficiently select and apply the right settings.
The carburizing program database is generated by the process simulation system, considering material composition, carburizing temperature, case depth, and surface carbon content. These programs are validated through production experience to ensure optimal results. The automated control system precisely manages carburizing temperature, pressure, gas flow rate, and pulse timing, ensuring the process meets carburizing or carbonitriding requirements with high accuracy and consistency.
Examples
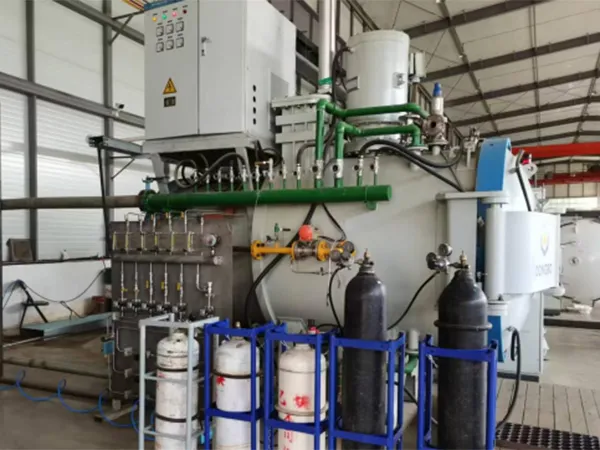
Horizontal Single Chamber Gas Quenching Low Pressure Vacuum Carburizing Furnace
Inquiry
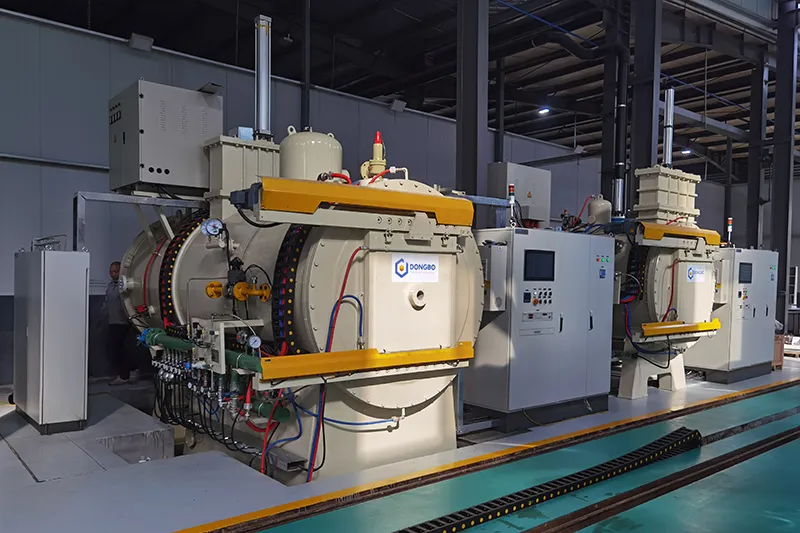
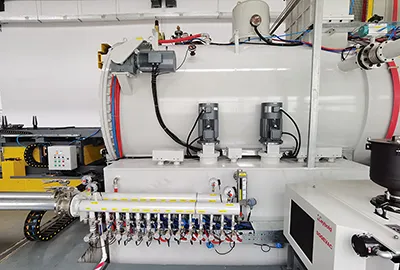
Horizontal Double Chamber Oil Quenching Low Pressure Vacuum Carburizing Furnace
Inquiry
Horizontal Double Chamber Gas Quenching Low Pressure Vacuum Carburizing Furnace
Inquiry
Horizontal Three Chamber Salt Bath Low Pressure Vacuum Carburizing Furnace
Inquiry
Vertical Single Chamber Gas Quenching Low Pressure Vacuum Carburizing Furnace
Inquiry
Commitments
- Capable of carburizing parts and products made from multi-component alloy and high-alloy materials, for example: 12Cr2Ni4A, 18Cr2Ni4WA, 20Cr2Ni4, 18CrNiMo7-6, and third-generation bearing steel (BG801), etc.
- High-level intelligent process: simply input the material grade, carburizing temperature, and case depth, and the system automatically generates and issues the carburizing process. It eliminates the need to calculate workpiece surface area, thus removes the requirement for dedicated carburizing specialists, reducing labor costs by at least USD 30,000 per year.
- The equipment generates only minimal carbon black during long-term continuous vacuum carburizing, ensuring uninterrupted production. Minor carbon-black cleaning can be performed during routine maintenance.
- The Vacuum Carburizing Process Expert System® provides flexible control of case hardness. It can design customized hardness gradients according to product requirements. Flexible carburizing control technology enables personalized surface hardness distribution within a defined range.
- The Vacuum Carburizing Process Expert System® includes a supplementary carburizing function. In the event of special on-site situations (such as power or gas interruptions), supplementary infiltration can be performed, effectively reducing user risk.
- The Vacuum Carburizing Process Expert System® supports processes and can perform carbonitriding according to the specific requirements of different customers. carbonitriding
Advantages of Low-Pressure Vacuum Carburizing Compared with Conventional Gas Carburizing
Low Pressure Vacuum Carburizing (Carbonitriding) Heat Treatment Line
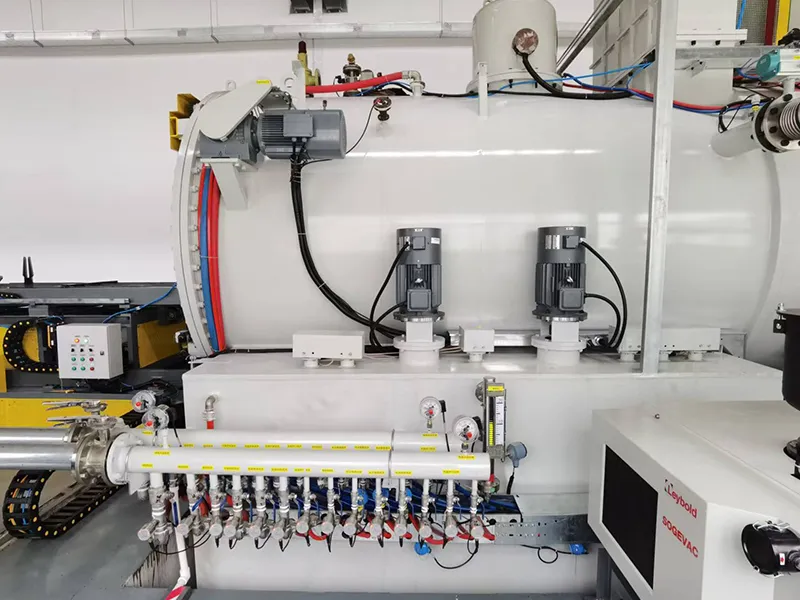
In addition to standalone units, we offer configurable external material handling systems that integrate multiple low-pressure vacuum carburizing (carbonitriding) furnaces, vacuum tempering furnaces, and various cleaning machines into a complete heat treatment line. This setup is designed to meet the demands of large-scale low-pressure vacuum carburizing and carbonitriding production, ensuring efficiency and seamless process integration.
Case Studies
DB-DCO1299H horizontal double chamber intelligent oil quenching low-pressure vacuum carburizing furnace with gas cooling, along with its complete auxiliary equipment package purchased by Hunan Changhang Power.
DB-DCO966H-III double chamber oil quenching low-pressure vacuum carburizing furnace with gas cooling purchased by Guangdong Litaifeng Technology.
DB-DCO966H-III oil quenching low-pressure vacuum carburizing production line purchased by Ningbo Intelligent Machine Tool Research Institute Co., Ltd. of China National Machinery Institute Group.
Our Featured Vacuum Furnaces